Introduction:
The Olmec civilization is one of the oldest in Mesoamerica, and its megalithic culture significantly influenced later civilizations like the Maya and Aztec.
However, the massive temples and stone monuments they constructed still hold many unresolved mysteries.
This article delves into the temples built by the Olmecs, exploring their origins and purposes in detail.
What is the Olmec Civilization?
The Olmec civilization flourished between 1200 BCE and 400 BCE along the Gulf Coast of present-day Mexico.
Known as the “Mother Culture of Mesoamerica,” they created massive stone sculptures and ceremonial artifacts, showcasing their advanced cultural development.
Their temple architecture served diverse purposes, including religious rituals and astronomical observations.
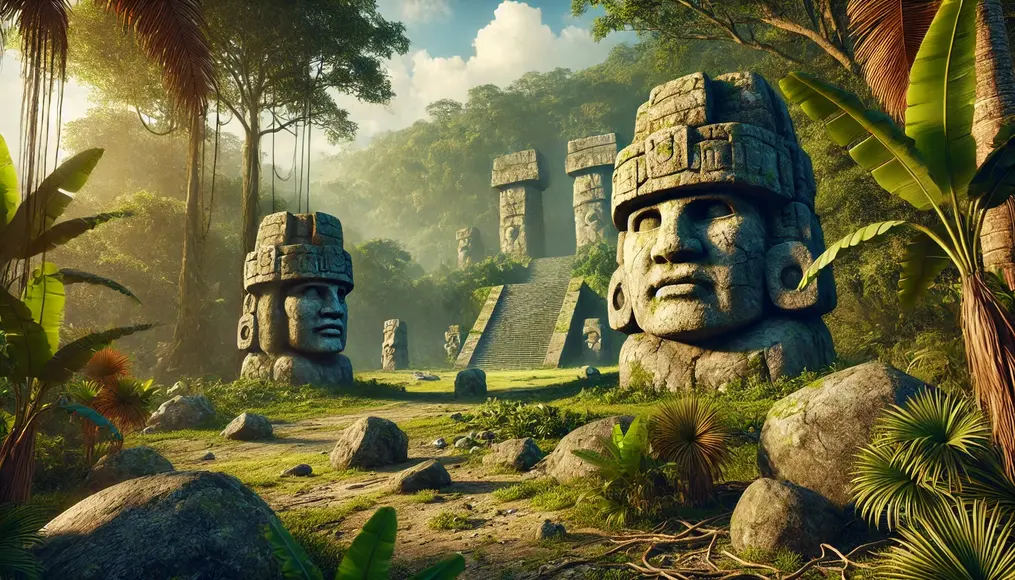

The Megalithic Culture and Its Technology
The Olmec civilization’s hallmark was its megalithic culture, which involved transporting and intricately carving stones weighing several tons.
These stone sculptures symbolized rulers or deities and served as focal points for religious ceremonies.
They were not merely decorative but likely played a role in astronomical observations and calendar creation.

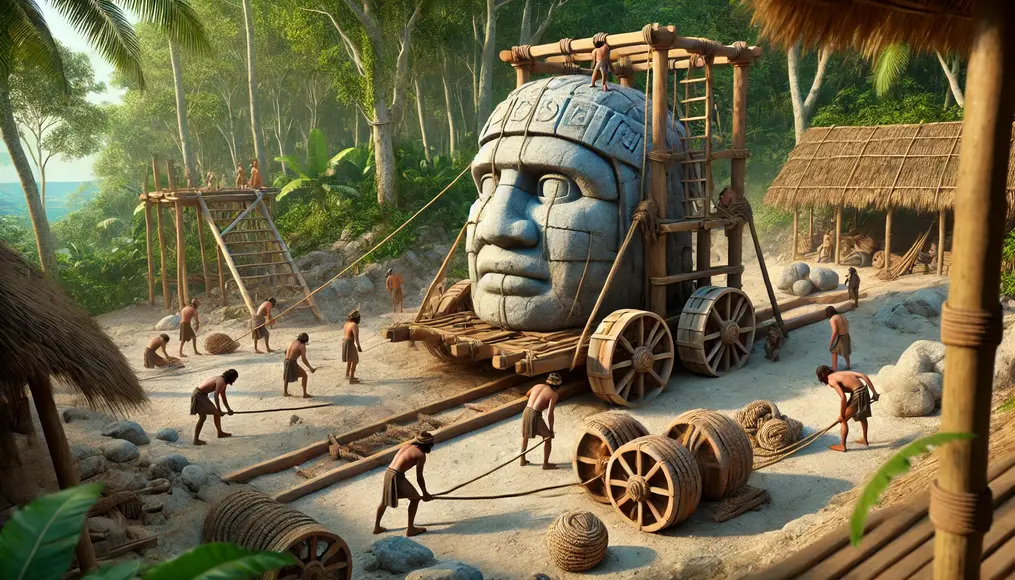
Revolutionary Stone Transportation Techniques
The Olmecs transported heavy stones over long distances, likely using ropes and wooden tools.
Despite their simplicity, these methods demonstrated exceptional precision and efficiency.
Their success highlights their advanced planning and knowledge, elevating their construction beyond mere brute force.

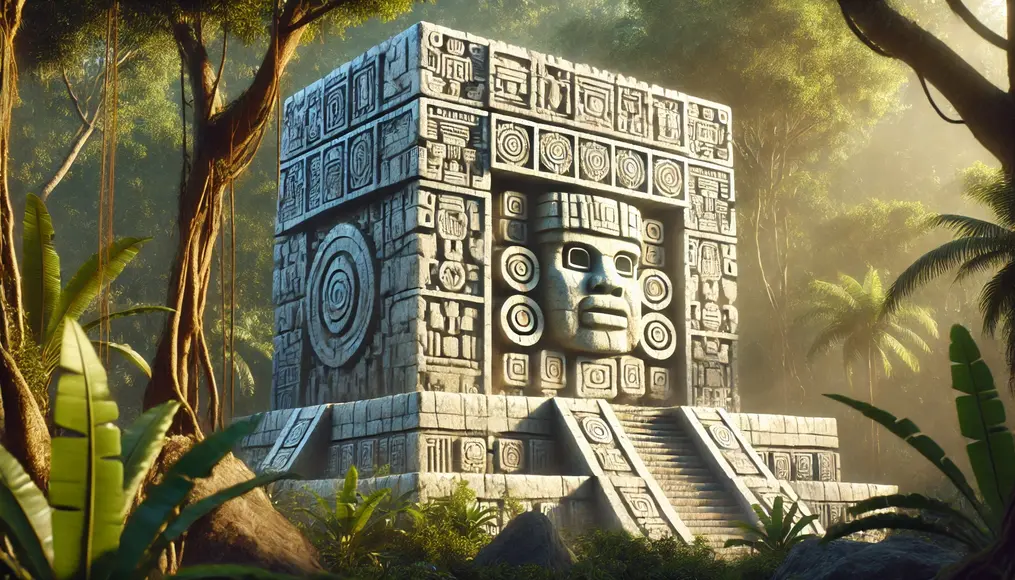
The Symbolism Behind Stone Carvings
Olmec stone carvings were far more than artistic expressions.
They symbolized rulers and gods, acting as focal points for religious rituals and social hierarchy.
Some carvings also had astronomical significance, revealing the Olmecs’ profound scientific understanding.
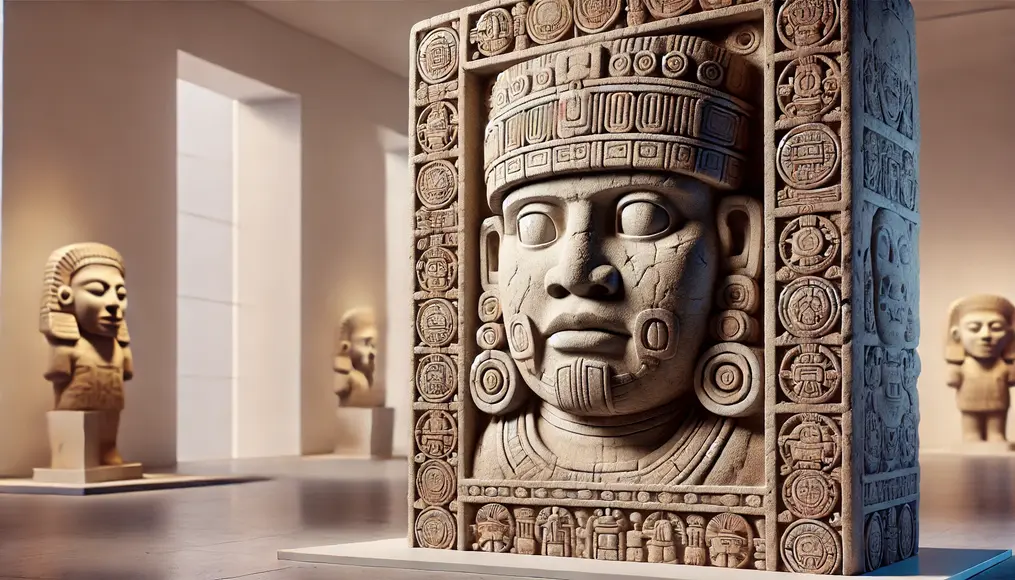

Functions and Architecture of Olmec Temples
The temples of the Olmec civilization were centers for religious rituals, political activities, and astronomical studies.
These multifaceted roles offer crucial insights into their societal structure and worldview.
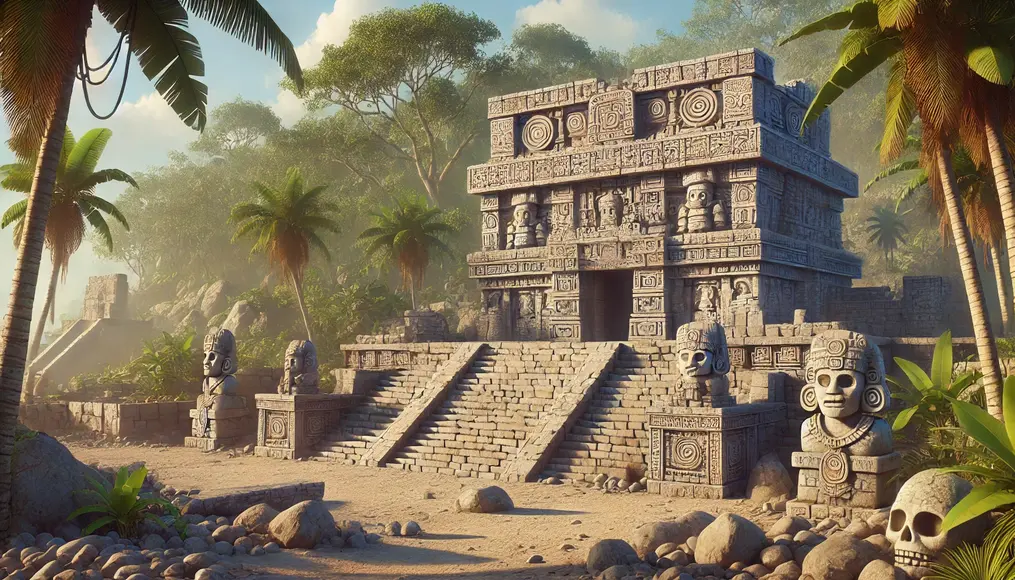

Temples as Centers of Ritual
The temples were sacred spaces for offering prayers and sacrifices to the gods.
Structures like the “Megalithic Altar” were used for rituals involving blood sacrifices and fire.
These ceremonies were believed to secure abundant harvests and favorable weather.
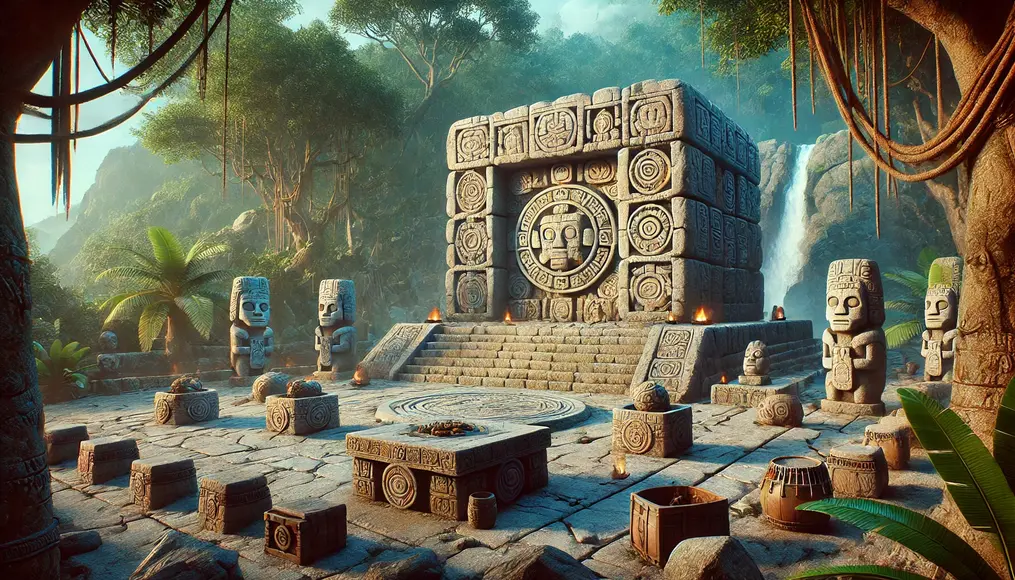

Astronomical Observation Hubs
The design and layout of the temples also served as tools for astronomical observations.
Their alignment with the sun and stars helped schedule agricultural activities and religious events.
This reveals the Olmecs’ sophisticated astronomical knowledge and its integration into their daily lives.

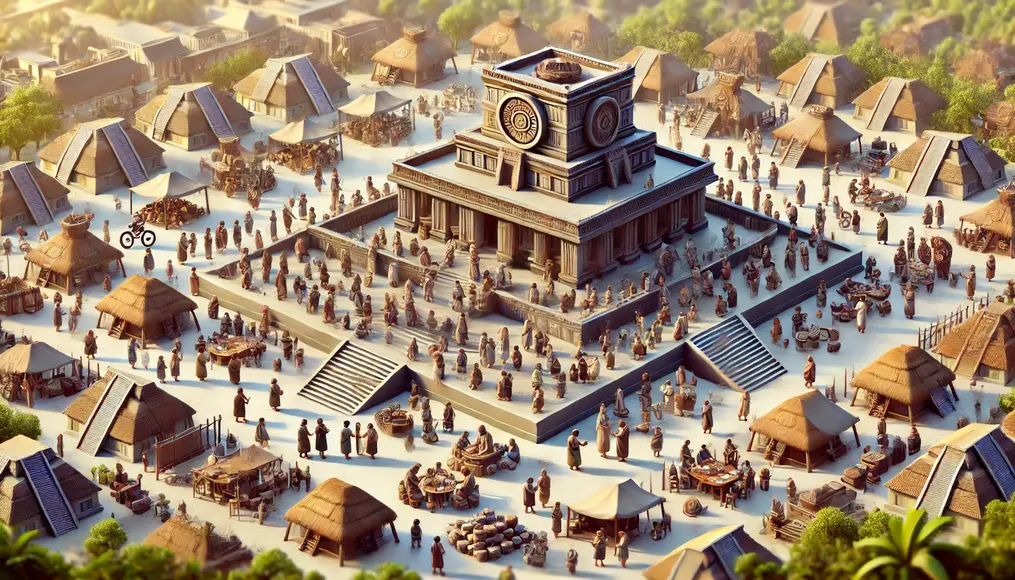
Temples as Symbols of Social Status
The grandeur of Olmec temples symbolized social status and power.
Their scale and splendor reflected the resources and labor mobilized by their leaders.
These structures reinforced unity and cohesion within the civilization.

Modern Significance of Olmec Temples
The megalithic temples of the Olmec civilization convey more than historical value.
Their construction techniques and astronomical insights remain astonishing even by modern standards.
Additionally, their harmonious relationship with nature serves as a timeless lesson for building sustainable societies today.
Conclusion
The temples of the Olmec civilization represent a fusion of religion, astronomy, and social structure.
Exploring their origins reveals the profound impact ancient civilizations have on modern society.
The ingenuity and determination reflected in these structures inspire us to continue our quest for understanding the unknown.
What are your thoughts on the Olmec civilization’s temples?
Feel free to share your opinions and insights in the comments below!




Comment