For humans, extreme cold environments are nearly unbearable.
Yet, there are microorganisms that manage to survive even in these freezing temperatures.
What makes these tiny organisms capable of living in such frigid conditions?
This article explores the survival mechanisms of microorganisms in extreme cold and the possibilities they reveal.
What Are Cold-Resistant Microbes?
Cold-resistant microbes are those that can survive and even thrive in sub-zero temperatures.
They are often found in extremely cold environments like Antarctica and deep-sea regions, living within freezing water or briny solutions.
- High Adaptability
They have evolved specialized proteins and cell membranes to adapt to these harsh conditions. - Reduced Metabolic Rate
At extremely low temperatures, their metabolism slows down significantly, allowing them to use energy efficiently to survive.
These organisms are also referred to as extremophiles, and they’re valuable subjects for research, particularly for understanding the possibility of extraterrestrial life.
How Microorganisms Survive in Extreme Cold
The survival of microbes in extreme cold involves several key mechanisms:
- Antifreeze Proteins
To prevent cell freezing, they secrete antifreeze proteins.
This helps prevent ice crystals from forming inside the cell. - Altered Lipid Membranes
By altering their cell membrane’s lipid composition, they prevent damage from freezing. - Entering Dormancy
In extreme cold, they enter a dormant state, sustaining life with minimal metabolism.
These mechanisms, developed through evolution, enable these microorganisms to maintain life even in harsh conditions.
The Implications of Cold-Resistant Microbes
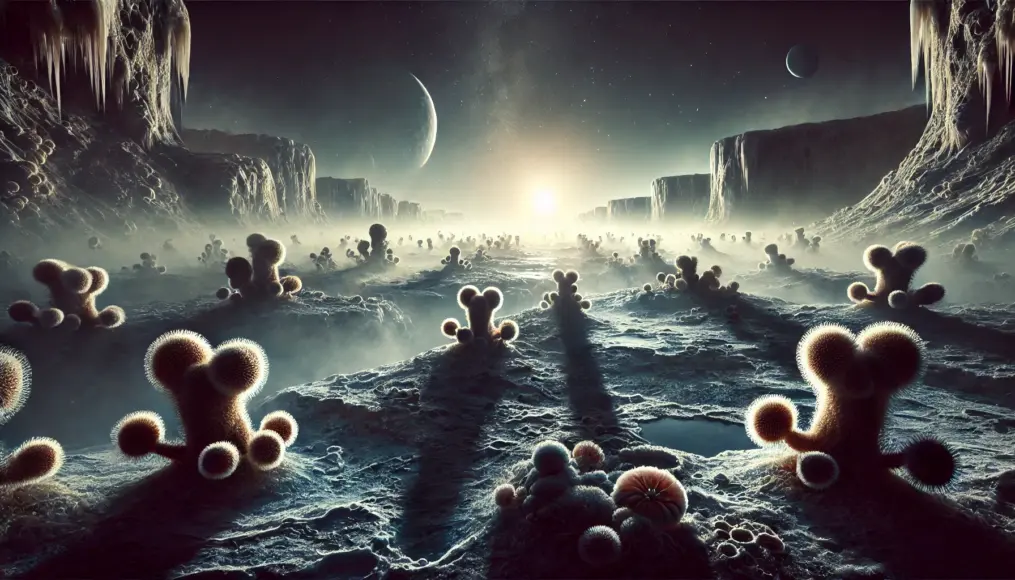

The existence of microbes that survive in extreme cold points to the potential for extraterrestrial life.
For instance, planets and moons with icy surfaces, like Mars and Europa (Jupiter’s moon), may host similar life forms.
- Potential for Space Exploration
The survival strategies of these microbes could offer valuable insights for space exploration.
They might inform the design of technology for exploring life in extreme environments in space. - Applications in Medicine and Biotechnology
Properties like antifreeze proteins could have applications in medicine and biotechnology.
The discovery of organisms that might survive in frozen extraterrestrial environments could reshape our understanding of life in the universe.
Summary
- Cold-resistant microbes adapt to extreme environments with specialized proteins and cell membranes.
- They protect themselves through antifreeze proteins and altered lipid membranes.
- Their existence points to the possibility of extraterrestrial life and offers potential for advancements in space exploration and medicine.
In this article, we’ve explored the remarkable resilience and mechanisms of microbes that survive in extreme cold.
These microorganisms symbolize a frontier of unknown possibilities.
As scientific research advances, we may uncover more mysteries and possibly find extraterrestrial life.
Through this article, we hope to inspire a sense of awe at the vast unknowns that still surround us.



Comment